Zero trust, XDR prominent in Gartner’s Hype Cycle for Endpoint Security
venturebeat.com – 2023-02-20 17:07:00 – Source link
Check out all the on-demand sessions from the Intelligent Security Summit here.
Every enterprise is in an endpoint security arms race. Attackers adapt their tactics faster than the most advanced security teams can react. One of the most compelling insights from comparing successive editions of Gartner’s Hype Cycle for Endpoint Security is how more CISOs are adopting extended detection and response (XDR) and zero trust network access (ZTNA) in response to escalating endpoint attacks.
XDR is also proving to be the technology many enterprises need to drive their tech stack consolidation initiatives. Vendors developing and selling solutions with the most pivotal technologies on the Hype Cycle are driving industry consolidation by cannibalizing the features of adjacent solutions in innovative ways.
Unified endpoint security (UES) vendors provide one example. They’re integrating endpoint operations and endpoint security workflows and tools to deliver more real-time visibility, earlier threat detection and faster remediation of threats. They’re also integrating UEM tools with endpoint security tooling, including endpoint protection platforms (EPP) and endpoint detection and response (EDR) for all devices, with mobile threat defense (MTD) providing telemetry data.
Growing adoption of XDR, zero trust for endpoint security
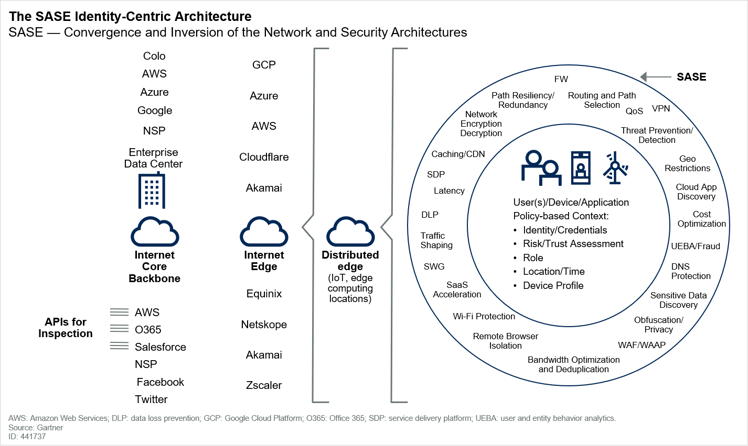
The Gartner Hype Cycle for Endpoint Security, 2022 reflects today’s surge in XDR and ZTNA adoption. Gartner is seeing enterprises adopt ZTNA as the foundation for building out security service edge (SSE) and secure access service edge (SASE).
Event
Intelligent Security Summit On-Demand
Learn the critical role of AI & ML in cybersecurity and industry specific case studies. Watch on-demand sessions today.
Watch Here
SSE and SASE have been market-tested. They can securely enable application access from any device over any network, with limited impact on users’ experiences. The many use cases virtual workforces have created are the fuel driving SSE and SASE adoption, which also ensures ZTNA’s continued growth.
Why zero trust is growing now
Gartner’s latest Information Security and Risk Management forecast predicts worldwide end-user spending on ZTNA systems and solutions will grow from $819.1 million in 2022 to $2.01 billion in 2026, achieving a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.6%. ZTNA is predicted to be one of the information security and risk management market’s fastest-growing segments, second only to cloud security and application security. Those markets are predicted to grow at compound annual growth rates of 24.6% and 22.6% respectively through 2026.
Foremost among ZTNA’s growth drivers is CISOs’ interest in upgrading legacy VPN systems. These systems assumed static locations, and secured connections to internal data centers. Most network traffic today is much more fluid, much of it occurring outside an enterprise. IT and security teams need hardened, secure and reliable connections to suppliers, vendors and contractors without exposing vulnerable internal apps over VPNs.
CISOs are piloting SSE and SASE and moving them into production. VentureBeat learned that CISOs are increasingly adding ZTNA to their SASE roadmaps. SSE vendors also integrate ZTNA functionality and components into their platforms for enterprises looking to create secure, reliable connections to internal, proprietary cloud services, apps and web platforms from a single platform or endpoint agent.
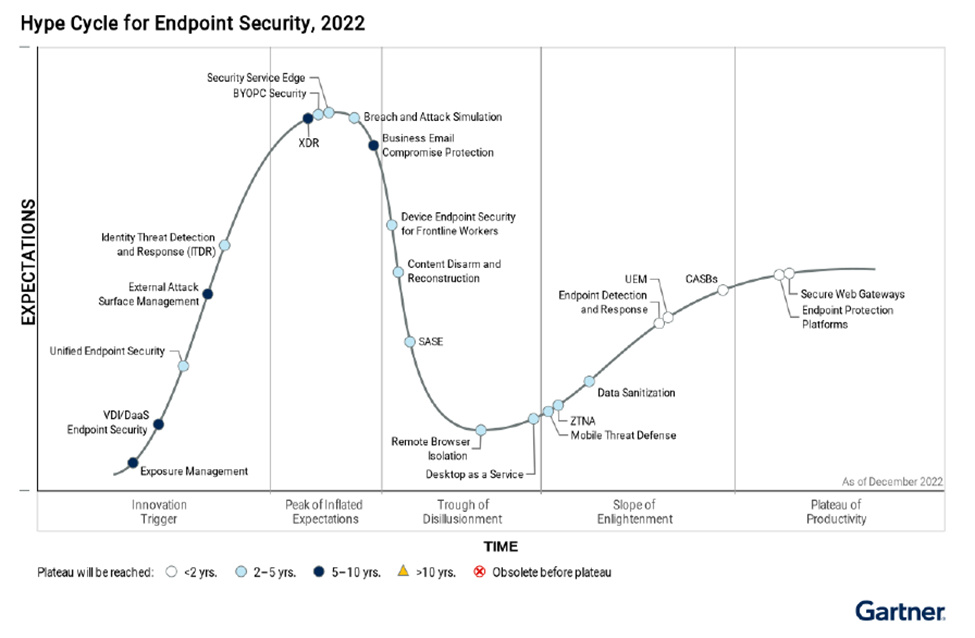
What’s new In Gartner’s Hype Cycle for Endpoint Security, 2022
There are 23 technologies on the Hype Cycle in 2022, up from 18 the previous year. Five technologies were added in 2022: exposure management, external attack surface management, breach and attack simulation, content disarm and reconstruction, and identity threat detection and response (ITDR). ITDR reflects the high priority CISOs are putting on becoming more cyber-resilient.
The following are some key insights from Gartner’s Hype Cycle for Endpoint Security, 2022:
ITDR is table stakes in a zero-trust world
With identities under siege and cyberattackers going after identity and access management (IAM), privileged access management (PAM) and active directories to take control of infrastructures in seconds, it’s understandable that Gartner’s clients are making ITDR a priority.
Gartner defines ITDR in the Hype Cycle report by saying, “Identity threat detection and response encompasses the tools and processes that protect the identity infrastructure from malicious attacks. They can discover and detect threats, evaluate policies, respond to threats, investigate potential attacks, and restore normal operation as needed.”
ITDR grew out of the need to harden the defenses protecting IAM, PAM and Active Directory Federation Services. Leading vendors include CrowdStrike, Microsoft, Netwrix, Quest, Semperis, SentinelOne, Silverfort, SpecterOps and Tenable.
Ransomware is forcing endpoint protection platforms (EPPs) to get smarter and stronger, fast
As the most prevalent threat surface, endpoints face a continuous stream of intrusion and breach attempts. More sophisticated ransomware attacks are driving faster innovation and greater cyber-resiliency in self-healing endpoints in endpoint protection platforms.
Gartner states in the Hype Cycle that “ransomware, in particular, has evolved from relatively simple automated methods to highly organized human-operated attacks to extract between 1% and 2% of corporate revenue as ransom.”
EPP providers rely on their cloud-native platforms to catalyze innovation. This starts with broader API integration options; support for behavior-based detection; and native analytics to the cloud platform capable of identifying and predicting potential threats. Leading EPP platform vendors include Broadcom (Symantec), Bitdefender, CrowdStrike, Cisco, Cybereason, Deep Instinct, Trellix, Microsoft, SentinelOne, Sophos, Trend Micro and VMware Carbon Black.
Self-healing endpoints have emerged as a valuable asset for IT and security teams because they minimize manual administrative tasks. For this reason they have been gaining traction as part of ZTNA frameworks. Leading providers of self-healing endpoints include Absolute Software, Akamai, Ivanti, Malwarebytes, McAfee, Microsoft 365, Qualys, SentinelOne, Tanium, Trend Micro and Webroot.
Protecting browser sessions and web apps with zero trust at scale
“Web applications are the number one vector and, not surprisingly, are connected to the high number of DoS attacks. This pairing, along with the use of stolen credentials (commonly targeting some form of a web application), is consistent with what we’ve seen for the past few years,” according to the 2022 Verizon Data Breach Report. 80% of all breaches get started in web applications with stolen access credentials, backdoor attacks, remote injection and desktop-sharing software hacks.
That’s why remote browser isolation (RBI) is gaining traction in enterprises, with devops teams integrating RBI into their apps as a safeguard against breaches.
Shutting down web-based attacks at the application and browser levels becomes urgent as an enterprise grows and relies more on outside contractors, partners and channels. Remote workers bring unmanaged devices into the mix. RBI serves as a control point for unmanaged devices to support sensitive-data protection. Cloud access security brokers (CASBs) and ZTNA offerings are now employing RBI for this use case.
It’s fascinating to see the pace and ingenuity of innovations in browser isolation today. Browser isolation is a technique that securely runs web apps by creating a gap between networks and apps on the one hand and malware on the other.
RBI runs every session in a secured, isolated cloud environment while enforcing least privileged application access in every browser session. That alleviates the need to install and track endpoint agents/clients across managed and unmanaged devices, and enables simple, secure BYOD access for employees and third-party contractors working on their own devices.
CISOs tell VentureBeat that RBI scales easily across their remote workforces, supplier networks and indirect sales channels because it’s browser-based and easy to configure. Every application access session can be configured to the specific level of security needed.
Cybersecurity teams are commonly using application isolation to define user-level policies that control which application a given user can access and which data-sharing actions they’re allowed to take.
The most common controls include DLP scanning, malware scanning, and limiting cut-and-paste functions, including clipboard use, file upload/download permissions, and permissions to enter data into text fields. Vendors that have adapted their RBI solutions to support application access security include Broadcom, Ericom and Zscaler.
The RBI approach also secures all of web apps’ exposed surfaces, protecting them from compromised devices and attackers while ensuring legitimate users have complete access. The air-gapping technique blocks hackers or infected machines from probing web apps seeking vulnerabilities to exploit, because they have no visibility to page source code, developer tools or APIs.
Achieving parity in the endpoint security arms race will be hard
The Hype Cycle shows the impressive gains made in innovation across ITDR, RBI, UES, XDR, ZTNA and other core technologies integral to endpoint security. The challenge for providers is to keep up the pace of innovation while aggregating and cannibalizing products from adjacent market areas in order to sell CISOs the idea that a consolidated tech stack brings greater efficiency, visibility and control.
Enterprises need to be aware of and choose from the technologies included in the Hype Cycle to secure one endpoint at a time, rather than going for an enterprise-wide deployment right away.
Zero trust is proving its value, and the most valuable takeaway from this year’s hype cycle is the solid evidence of ZTNA and XDR gaining momentum across the enterprise.
VentureBeat’s mission is to be a digital town square for technical decision-makers to gain knowledge about transformative enterprise technology and transact. Discover our Briefings.





