Remote Work Brings User Complaints and High IT Costs
securityboulevard.com – 2021-07-07 15:30:48 – Source link
A recent “Work From Anywhere” survey commissioned by Cato Networks revealed that IT has encountered many unexpected challenges supporting and securing remote users in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. The survey, which queried some 2,686 IT leaders, found a host of operational and budgetary challenges.
“Work from anywhere has shifted business focus from the place of work to the users and the work they need to do,” said Eyal Webber-Zvik, vice president of product marketing at Cato Networks. “This shift created a whole slew of operational and budgetary challenges for IT in service delivery, access optimization and pervasive security that are designed around locations rather than people. We are now able to identify these issues and address them.”
The survey further revealed that the overall perception of how IT users work and are supported has changed. The pandemic forced many enterprises to shift to a remote work model, where users were moved from a managed location to remote or work from home (WFH) offices. Organizations invested in existing security and remote technologies to meet immediate needs. Technologies, such as centralized VPN servers, were used by 42% of respondents to initially support WFH initiatives. What’s more, some 40% of respondents indicated that, today, they backhaul remote access traffic to a hub or VPN concentrator to meet remote user needs, indicating a wholesale change in how end users connect to enterprise resources.
“The pandemic has shown us that businesses are no longer tied to a specific office or location,” Webber-Zvik stated. “By implementing a work-from-anywhere model, businesses are transitioning to a more efficient and collaborative way of doing business, allowing them to better meet the needs of their customers, as well as their employees.”
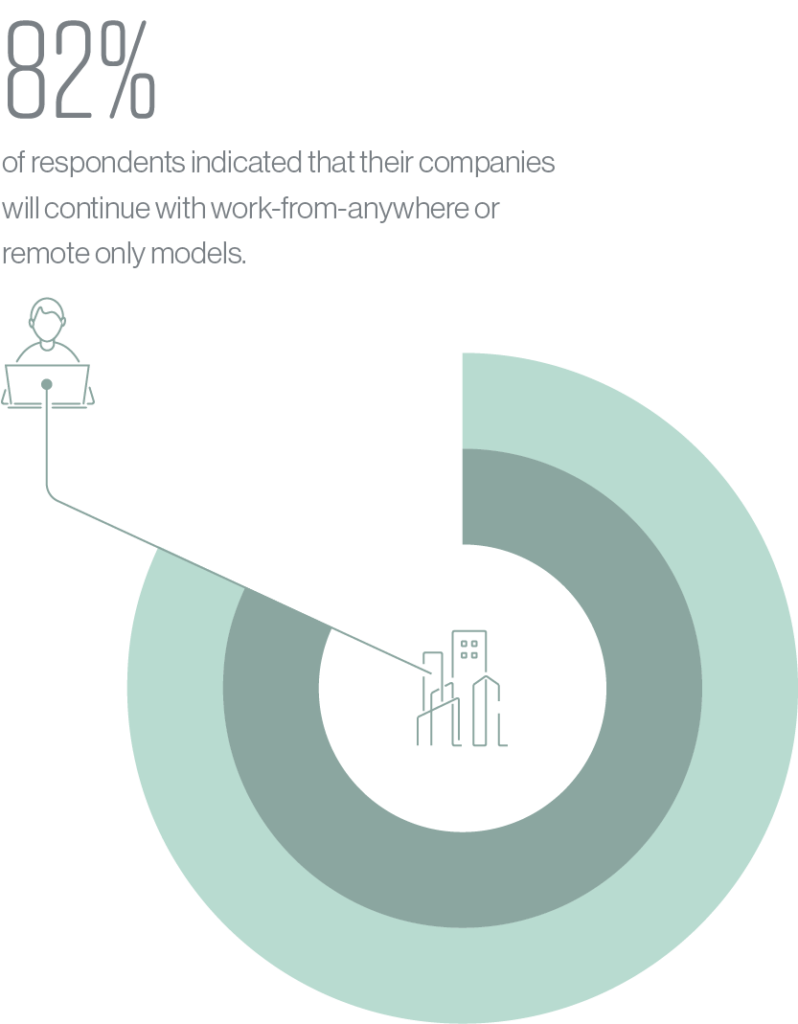
The survey also revealed that in the post-pandemic world, enterprises are looking to continue leveraging WFH ideologies. For example, some 82% of respondents indicated that their companies would continue with work-from-anywhere or remote only models. This is reflected in their priorities post-pandemic. Providing secure internet access everywhere continues to be the top priority for 67% of respondents.
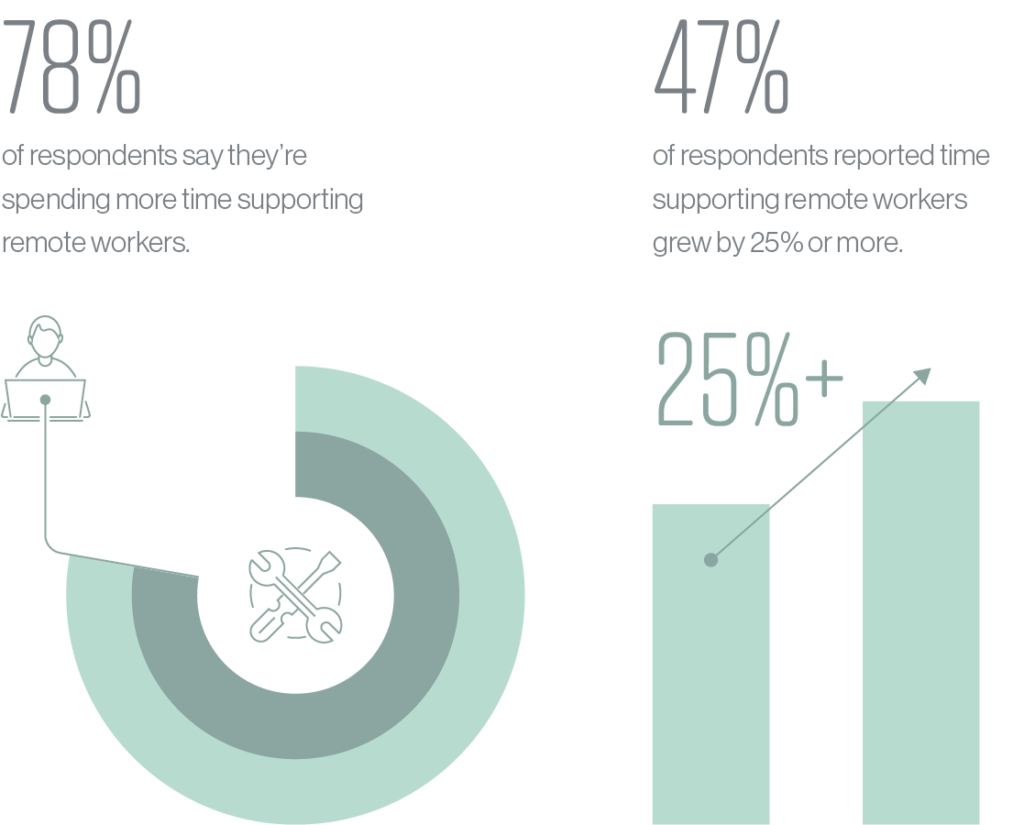
Despite the business advantages of a hybrid working model, there are some hurdles and costs that IT is quickly becoming aware of, impacting how they provision and support new working models. For instance, 78% of respondents say they’re spending more time supporting remote workers, while 47% of respondents reported their time spent supporting remote workers grew by 25% or more.
The data implied that those challenges arise from supporting legacy networks where remote traffic is backhauled to a centralized VPN server. In those environments, remote user complaints soared to 83% of respondents, versus 45% of respondents sending traffic to local security appliances or services.
“The pandemic has shown us that businesses are no longer tied to a specific office or location,” Webber-Zvik said. “By implementing a work from anywhere model, businesses are transitioning to a more efficient and collaborative way of doing business, allowing them to better meet the needs of their customers, as well as their employees.”
The survey also revealed concerns with service delivery, with 50% of those polled indicating that users complained about connection instability and 27% reported complaints about poor voice or video quality. Slow application response was another common remote user complaint, with 37% of respondents citing that as an issue.
Indications of service delivery issues over backhaul connections were noted by 30% of respondents who reported application performance for remote users was worse than for those in the office, versus 22% for those not backhauling traffic.
Security proved to be another major concern for respondents, with 44% of respondents indicating they could not provide remote workers with the same level of security for all traffic as their office counterparts. More than 80% of respondents said they were unable to provide the same level of security for remote workers for internet traffic and WAN traffic as they could for office workers.
From Webber-Zvick’s perspective, the survey indicates that enterprises need to rethink their remote connectivity strategies and leverage newer technologies, such as SASE. “Instead of spending weeks or months updating legacy infrastructure and updating remote workers’ software applications, SASE enables IT departments to install new applications and security protocols in minutes across the entire network. This not only saves time, but it also reduces overall costs and ensures adoption across all platforms and remote access points,” Webber-Zvik said.
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), a term coined by Gartner, is an extension of SD-WAN technology, which Gartner describes as a way for enterprises to enable infrastructure and operations (I&O) and security teams to deliver consistent, integrated and secure networking and security services to support digital business transformation, edge computing and workforce mobility.
Whether or not SASE is the best way to solve the problems presented by WFH or other remote use cases is still up for debate. However, the survey does offer evidence that enterprises must deal with certain cybersecurity and connectivity challenges one way or another if they wish to meet hybrid, remote and in-office user support expectations.



